
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Lifestyle
- Changes in Patterns of Physical Activity and Risk of Heart Failure in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):327-336. Published online November 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0046
- 5,381 View
- 210 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
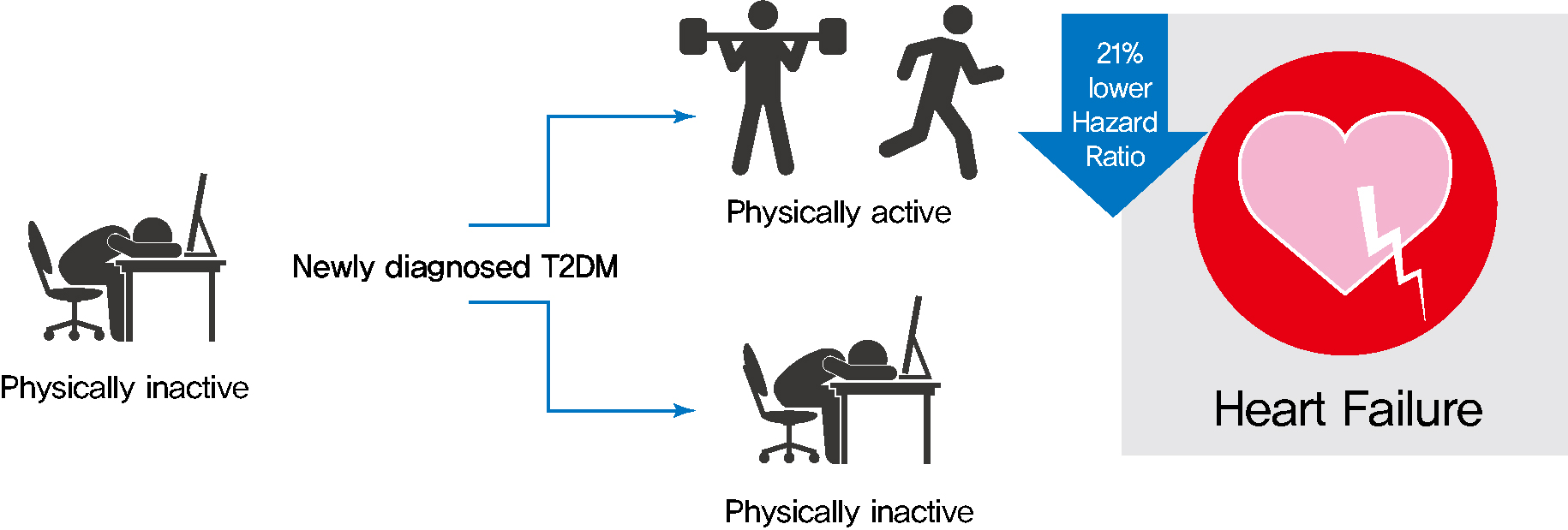
Exercise is recommended for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients to prevent cardiovascular disease. However, the effects of physical activity (PA) for reducing the risk of heart failure (HF) has yet to be elucidated. We aimed to assess the effect of changes in patterns of PA on incident HF, especially in newly diagnosed diabetic patients.
Methods
We examined health examination data and claims records of 294,528 participants from the Korean National Health Insurance Service who underwent health examinations between 2009 and 2012 and were newly diagnosed with T2DM. Participants were classified into the four groups according to changes in PA between before and after the diagnosis of T2DM: continuously inactive, inactive to active, active to inactive, and continuously active. The development of HF was analyzed until 2017.
Results
As compared with those who were continuously inactive, those who became physically active after diagnosis showed a reduced risk for HF (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66 to 0.93). Those who were continuously active had the lowest risk for HF (aHR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62 to 0.96). As compared with those who were inactive, those who exercised regularly, either performing vigorous or moderate PA, had a lower HF risk (aHR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.69 to 0.91).
Conclusion
Among individuals with newly diagnosed T2DM, the risk of HF was reduced in those with higher levels of PA after diagnosis was made. Our results suggest either increasing or maintaining the frequency of PA after the diagnosis of T2DM may lower the risk of HF. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kyoung Min Kim, Kyoung Jin Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yumie Rhee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1194. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Association of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and frailty in community-dwelling older adults
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Eyun Song, Min Jeong Park, Hye Jin Yoo, Sei Hyun Baik, Miji Kim, Chang Won Won, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The associations between changes in hepatic steatosis and heart failure and mortality: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Dose-Dependent Effect of Smoking on Risk of Diabetes Remains after Smoking Cessation: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
- Se Eun Park, Mi Hae Seo, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Yang-Hyun Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):539-546. Published online March 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0061
- 7,691 View
- 188 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
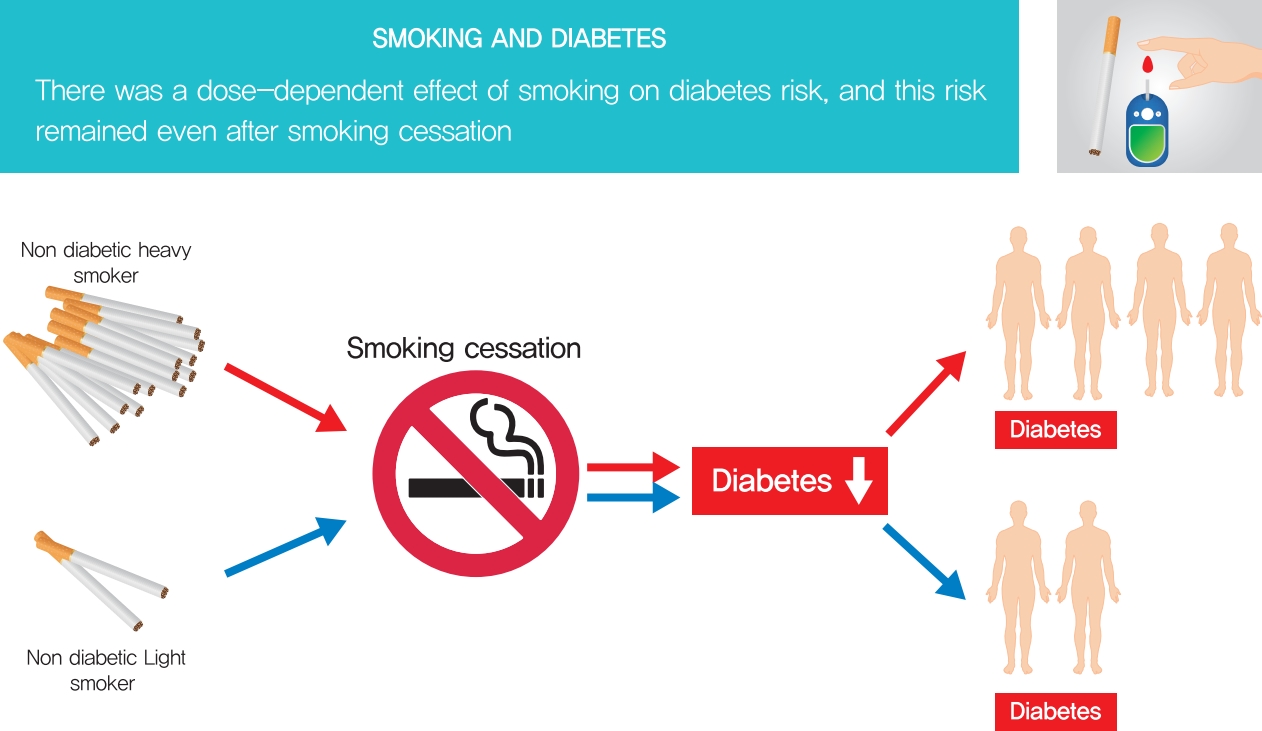
This study aimed to evaluate the dose-dependent effects of smoking on risk of diabetes among those quitting smoking.
Methods
We analyzed clinical data from a total of 5,198,792 individuals age 20 years or older who received health care check-up arranged by the national insurance program of Korea between 2009 and 2016 using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. Cumulative smoking was estimated by pack-years. Smokers were classified into four categories according to the amount of smoking: light smokers (0.025 to 5 smoking pack-years), medium smokers (5 to 14 smoking pack-years), heavy smokers (14 to 26 smoking pack-years), and extreme smokers (more than 26 smoking pack-years).
Results
During the study period, 164,335 individuals (3.2% of the total population) developed diabetes. Compared to sustained smokers, the risk of diabetes was significantly reduced in both quitters (hazard ratio [HR], 0.858; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.838 to 0.878) and nonsmokers (HR, 0.616; 95% CI, 0.606 to 0.625) after adjustment for multiple risk factors. The risk of diabetes gradually increased with amount of smoking in both quitters and current smokers. The risk of diabetes in heavy (HR, 1.119; 95% CI, 1.057 to 1.185) and extreme smokers (HR, 1.348; 95% CI, 1.275 to 1.425) among quitters was much higher compared to light smokers among current smokers.
Conclusion
Smoking cessation was effective in reducing the risk of diabetes regardless of weight change. However, there was a potential dose-dependent association between smoking amount and the development of diabetes. Diabetes risk still remained in heavy and extreme smokers even after smoking cessation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary and other lifestyle factors and their influence on non-communicable diseases in the Western Pacific region
Xiaomin Sun, Dong Keon Yon, Tuan Thanh Nguyen, Kumpei Tanisawa, Kumhee Son, Ling Zhang, Jing Shu, Wen Peng, Yuexin Yang, Francesco Branca, Mark L. Wahlqvist, Hyunjung Lim, Youfa Wang
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific.2024; 43: 100842. CrossRef - The Concentrations of Interleukin-6, Insulin, and Glucagon in the Context of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in IL6 and INS Genes
Magdalena Król-Kulikowska, Iwona Urbanowicz, Marta Kepinska, Mayank Choubey
Journal of Obesity.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Chronic cigarette smoking is associated with increased arterial stiffness in men and women: evidence from a large population-based cohort
Omar Hahad, Volker H. Schmitt, Natalie Arnold, Karsten Keller, Jürgen H. Prochaska, Philipp S. Wild, Andreas Schulz, Karl J. Lackner, Norbert Pfeiffer, Irene Schmidtmann, Matthias Michal, Jörn M. Schattenberg, Oliver Tüscher, Andreas Daiber, Thomas Münzel
Clinical Research in Cardiology.2023; 112(2): 270. CrossRef - Association between Meal Frequency and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Rural Adults: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study
Bota Baheti, Xiaotian Liu, Mu Wang, Caiyun Zhang, Xiaokang Dong, Ning Kang, Linlin Li, Xing Li, Songcheng Yu, Jian Hou, Zhenxing Mao, Chongjian Wang
Nutrients.2023; 15(6): 1348. CrossRef - Impaired Lung Function and Lung Cancer Incidence: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hye Seon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Seung Hoon Kim, Shin Young Kim, Chi Hong Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sung Kyoung Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(4): 1077. CrossRef - Smoking cessation and risk of type 2 diabetes
Jana Malinovská, Jana Urbanová, Veronika Vejtasová, Alexandra Romanová, Sabina Pálová, Syed Taha Naeem, Jan Brož
Vnitřní lékařství.2022; 68(1): E04. CrossRef - Association between lung function and the risk of atrial fibrillation in a nationwide population cohort study
Su Nam Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sung-Ho Her, Kyungdo Han, Donggyu Moon, Sung Kyoung Kim, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yu-Bae Ahn
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex differences in factors associated with prediabetes in Korean adults
Jin Suk Ra
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2022; 13(2): 142. CrossRef - Smoking and diabetes interplay: A comprehensive review and joint statement
Vincent Durlach, Bruno Vergès, Abdallah Al-Salameh, Thibault Bahougne, Farid Benzerouk, Ivan Berlin, Carole Clair, Jacques Mansourati, Alexia Rouland, Daniel Thomas, Philippe Thuillier, Blandine Tramunt, Anne-Laurence Le Faou
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(6): 101370. CrossRef - Impact of healthy lifestyle on the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in southwest China: A prospective cohort study
Yanli Wu, Xi He, Jie Zhou, Yiying Wang, Lisha Yu, Xuejiao Li, Tao Liu, Jianhua Luo
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(12): 2091. CrossRef - Current status of health promotion in Korea
Soo Young Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(12): 776. CrossRef - Smoking Cessation after Diagnosis of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation and the Risk of Stroke and Death
So-Ryoung Lee, Eue-Keun Choi, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Seil Oh, Gregory Y. H. Lip
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(11): 2238. CrossRef
- Dietary and other lifestyle factors and their influence on non-communicable diseases in the Western Pacific region
- Cardiovascular risk/Epidemiology
- Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in Patients with Diabetes and Coexisting Depression: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):379-389. Published online December 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0008
- 7,496 View
- 235 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
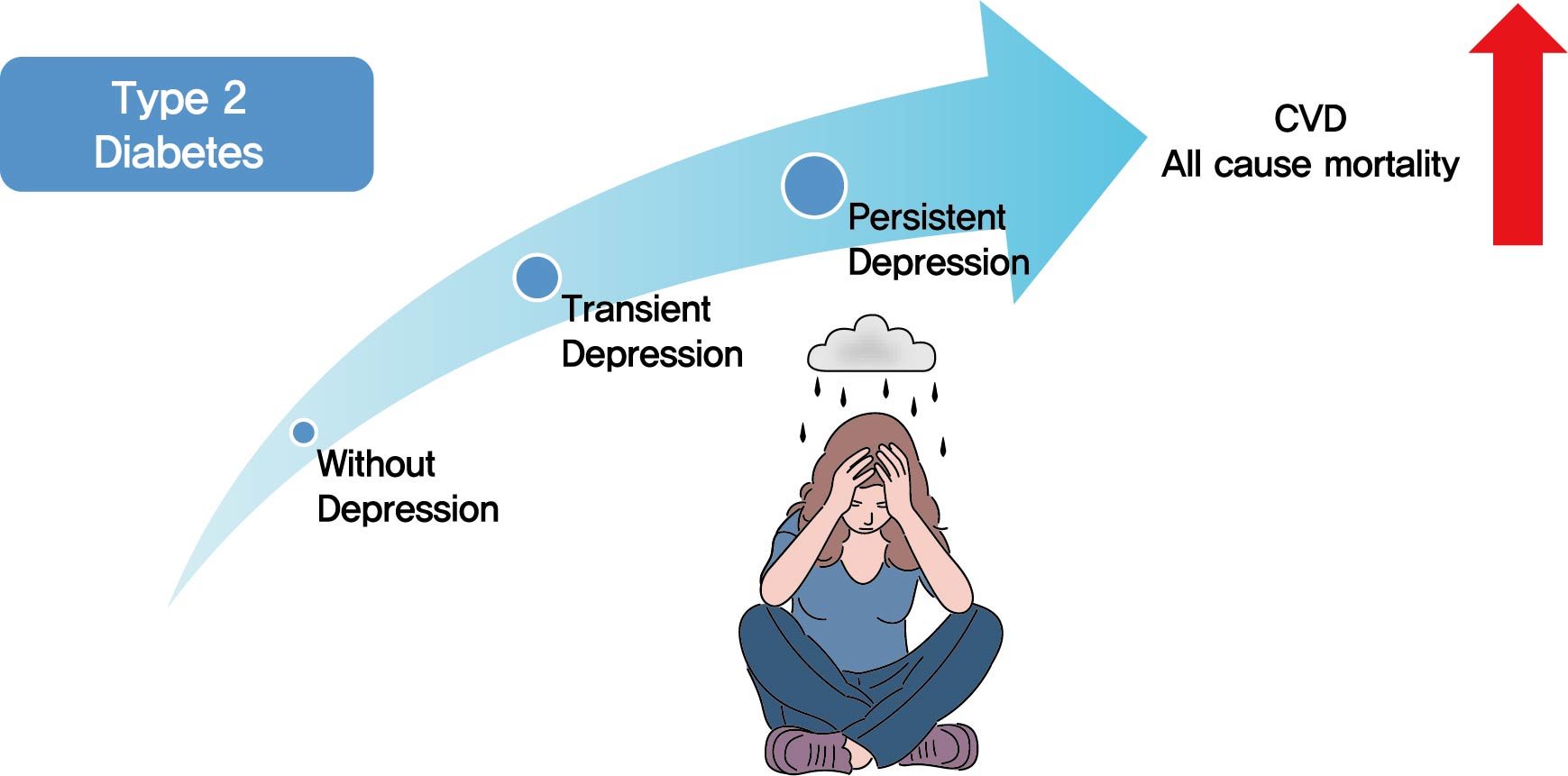
Previous studies have suggested that depression in patients with diabetes is associated with worse health outcomes. The aim of this study was to evaluate the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality in patients with diabetes with comorbid depression.
Methods
We examined the general health check-up data and claim database of the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) of 2,668,615 participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus who had examinations between 2009 and 2012. As NHIS database has been established since 2002, those who had been diagnosed with depression or CVD since 2002 were excluded. The 2,228,443 participants were classified into three groups according to the claim history of depression; normal group (n=2,166,979), transient depression group (one episode of depression, n=42,124) and persistent depression group (at least two episodes of depression, n=19,340). The development of CVD and mortality were analyzed from 2009 to 2017.
Results
Those with depression showed a significantly increased risk for stroke (transient depression group: hazard ratio [HR], 1.20; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.15 to 1.26) (persistent depression group: HR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.46 to 1.63). Those with depression had an increased risk for myocardial infarction (transient depression group: HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.18 to 1.31) (persistent depression group: HR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.29 to 1.49). The persistent depression group had an increased risk for all-cause mortality (HR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.60 to 1.72).
Conclusion
Coexisting depression in patients with diabetes has a deleterious effect on the development of CVD and mortality. We suggest that more attention should be given to patients with diabetes who present with depressive symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychological resilience mediates the relationship between diabetes distress and depression among persons with diabetes in a multi-group analysis
Ajele Kenni Wojujutari, Erhabor Sunday Idemudia, Lawrence Ejike Ugwu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating effect of depression on new-onset stroke in diabetic population: Evidence from the China health and retirement longitudinal study
Gege Jiang, Yaoling Wang, Liping Wang, Minfang Chen, Wei Li
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 321: 208. CrossRef - Frailty and outcomes in lacunar stroke
Sima Vazquez, Zehavya Stadlan, Justin M Lapow, Eric Feldstein, Smit Shah, Ankita Das, Alexandria F Naftchi, Eris Spirollari, Akash Thaker, Syed Faraz Kazim, Jose F Dominguez, Neisha Patel, Christeena Kurian, Ji Chong, Stephan A Mayer, Gurmeen Kaur, Chirag
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2023; 32(2): 106942. CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - The Association between Dietary Carotenoid Intake and Risk of Depression among Patients with Cardiometabolic Disease
Jie Liang, Yuhao Wang, Min Chen
International Heart Journal.2023; 64(2): 223. CrossRef - Associations of concomitant retinopathy and depression with mortality in a nationally representative population
Zheng Lyu, Yilin Chen, Zhuoting Zhu, Xiaoyang Luo, Ying Cui, Jie Xie, Zhifan Chen, Junbin Liu, Xiyu Wu, Gabrella Bulloch, Qianli Meng
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 336: 15. CrossRef - Clinical insights into the cross-link between mood disorders and type 2 diabetes: A review of longitudinal studies and Mendelian randomisation analyses
Chiara Possidente, Giuseppe Fanelli, Alessandro Serretti, Chiara Fabbri
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2023; 152: 105298. CrossRef - Prevalence of depression and association with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among individuals with type 2 diabetes: a cohort study based on NHANES 2005–2018 data
Zhen Feng, Wai Kei Tong, Xinyue Zhang, Zhijia Tang
BMC Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cholecystectomy Increases the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in the Korean Population
Ji Hye Huh, Kyong Joo Lee, Yun Kyung Cho, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung-do Han, Dong Hee Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Annals of Surgery.2023; 278(2): e264. CrossRef - Risk of depression in patients with acromegaly in Korea (2006-2016): a nationwide population-based study
Shinje Moon, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
European Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 189(3): 363. CrossRef - The association between cardiovascular drugs and depression/anxiety in patients with cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis
Lijun Zhang, Yanping Bao, Shuhui Tao, Yimiao Zhao, Meiyan Liu
Pharmacological Research.2022; 175: 106024. CrossRef - Association of mental health with the risk of coronary artery disease in patients with diabetes: A mendelian randomization study
Teng Hu, Fangkun Yang, Kewan He, Jiajun Ying, Hanbin Cui
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(3): 703. CrossRef - Comorbidity of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Depression: Clinical Evidence and Rationale for the Exacerbation of Cardiovascular Disease
Mengmeng Zhu, Yiwen Li, Binyu Luo, Jing Cui, Yanfei Liu, Yue Liu
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding and Utilizing Claim Data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and Health Insurance Review & Assessment (HIRA) Database for Research
Dae-Sung Kyoung, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(2): 103. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - Evaluation of rosmarinic acid against myocardial infarction in maternally separated rats
Himanshu Verma, Anindita Bhattacharjee, Naveen Shivavedi, Prasanta Kumar Nayak
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2022; 395(10): 1189. CrossRef - Lipid cutoffs for increased cardiovascular disease risk in non-diabetic young people
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 29(14): 1866. CrossRef - Risk factors associated with mortality among individuals with type 2 diabetes and depression across two cohorts
Christopher Rohde, Jens Steen Nielsen, Jakob Schöllhammer Knudsen, Reimar Wernich Thomsen, Søren Dinesen Østergaard
European Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 187(4): 567. CrossRef - Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in Patients with Diabetes and Coexisting Depression: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:379-89)
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 789. CrossRef - Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in Patients with Diabetes and Coexisting Depression: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:379-89)
Inha Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 793. CrossRef - Affective Temperament and Glycemic Control – The Psychological Aspect of Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus
Natalia Lesiewska, Anna Kamińska, Roman Junik, Magdalena Michalewicz, Bartłomiej Myszkowski, Alina Borkowska, Maciej Bieliński
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4981. CrossRef
- Psychological resilience mediates the relationship between diabetes distress and depression among persons with diabetes in a multi-group analysis
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
-
- Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):592-601. Published online April 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0104
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2020;44(5):783

- 6,635 View
- 142 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Recent studies suggest an association between diabetes and increased risk of heart failure (HF). However, the associations among obesity status, glycemic status, and risk of HF are not known. In this study, we analyzed whether the risk of HF increases in participants according to baseline glycemic status and whether this increased risk is associated with obesity status.
Methods We analyzed the risk of HF according to baseline glycemic status (normoglycemia, impaired fasting glucose [IFG], and diabetes) in 9,720,220 Koreans who underwent Korean National Health Screening in 2009 without HF at baseline with a median follow-up period of 6.3 years. The participants were divided into five and six groups according to baseline body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference, respectively.
Results Participants with IFG and those with diabetes showed a 1.08- and 1.86-fold increased risk of HF, respectively, compared to normoglycemic participants. Compared to the normal weight group (BMI, 18.5 to 22.9 kg/m2), the underweight group (BMI <18.5 kg/m2) showed a 1.7-fold increased risk of HF, and those with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 showed a 1.1-fold increased risk of HF, suggesting a J-shaped association with BMI. When similar analyses were performed for different glycemic statuses, the J-shaped association between BMI and HF risk was consistently observed in both groups with and without diabetes.
Conclusion Participants with IFG and diabetes showed a significantly increased HF risk compared to normoglycemic participants. This increased risk of HF was mostly prominent in underweight and class II obese participants than in participants with normal weight.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung‐Do Han, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 671. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Research on obesity using the National Health Information Database: recent trends
Eun-Jung Rhee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(2): 35. CrossRef - Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential Impact of Obesity on the Risk of Diabetes Development in Two Age Groups: Analysis from the National Health Screening Program
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Yang-Hyun Kim, Ga Eun Nam, Sang Hyun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 846. CrossRef - Characterization of the oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in metabolically healthy obese individuals
Hazhmat Ali
Al-Kufa University Journal for Biology.2023; 15(3): 28. CrossRef - The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - Changes in Patterns of Physical Activity and Risk of Heart Failure in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 327. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - Impact of hypoglycemia at the time of hospitalization for heart failure from emergency department on major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with and without type 2 diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Gee-Hee Kim, Yu-Bae Ahn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin resistance and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Pathogenetic and therapeutic crossroads
O. V. Tsygankova, N. E. Evdokimova, V. V. Veretyuk, L. D. Latyntseva, A. S. Ametov
Diabetes mellitus.2022; 25(6): 535. CrossRef - The association between metabolic syndrome and heart failure in middle-aged male and female: Korean population-based study of 2 million individuals
Tae-Eun Kim, Hyeongsu Kim, JiDong Sung, Duk-Kyung Kim, Myoung-Soon Lee, Seong Woo Han, Hyun-Joong Kim, Sung Hea Kim, Kyu-Hyung Ryu
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022078. CrossRef - Diabetes and Heart Failure
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(1): 12. CrossRef - Prediabetes and the risk of heart failure: A meta‐analysis
Xiaoyan Cai, Xiong Liu, Lichang Sun, Yiting He, Sulin Zheng, Yang Zhang, Yuli Huang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(8): 1746. CrossRef - Diabetes and Heart Failure
Eun-Jung Rhee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(2): 21. CrossRef - Effects of Lipid Overload on Heart in Metabolic
Diseases
An Yan, Guinan Xie, Xinya Ding, Yi Wang, Liping Guo
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2021; 53(12): 771. CrossRef - Obesity Degree and Glycemic Status: Factors That Should Be Considered in Heart Failure
Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 529. CrossRef - Letter: Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:592-601)
Darae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 777. CrossRef - Response: Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:592-601)
Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 781. CrossRef
- Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
- Epidemiology
- Relation between Baseline Height and New Diabetes Development: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se-Eun Park, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):794-803. Published online March 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0184
- 4,866 View
- 59 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Short stature and leg length are associated with risk of diabetes and obesity. However, it remains unclear whether this association is observed in Asians. We evaluated the association between short stature and increased risk for diabetes using the Korean National Health Screening (KNHS) dataset.
Methods We assessed diabetes development in 2015 in 21,122,422 non-diabetic Koreans (mean age 43 years) enrolled in KNHS from 2009 to 2012 using International Classification of Diseases 10th (ICD-10) code and anti-diabetic medication prescription. Risk was measured in age- and sex-dependent quintile groups of baseline height (20 to 39, 40 to 59, ≥60 years).
Results During median 5.6-year follow-up, 532,918 cases (2.5%) of diabetes occurred. The hazard ratio (HR) for diabetes development gradually increased from the 5th (reference) to 1st quintile group of baseline height after adjustment for confounding factors (1.000, 1.076 [1.067 to 1.085], 1.097 [1.088 to 1.107], 1.141 [1.132 to 1.151], 1.234 [1.224 to 1.244]), with similar results in analysis by sex. The HR per 5 cm height increase was lower than 1.00 only in those with fasting blood glucose (FBG) below 100 mg/dL (0.979 [0.975 to 0.983]), and in lean individuals (body mass index [BMI] 18.5 to 23 kg/m2: 0.993 [0.988 to 0.998]; BMI <18.5 kg/m2: 0.918 [0.9 to 0.935]).
Conclusion Height was inversely associated with diabetes risk in this nationwide study of Korean adults. This association did not differ by sex, and was significant in lean individuals and those with normal FBG levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung‐Do Han, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 671. CrossRef - Upper arm length and knee height are associated with diabetes in the middle-aged and elderly: evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Bingjie He, Zhengyang Li, Lu Xu, Lili Liu, Shengfeng Wang, Siyan Zhan, Yongfeng Song
Public Health Nutrition.2023; 26(1): 190. CrossRef - Anthropometric indexes and cardiovascular risk in Ecuadorian university students: A comparison with international references
Silvia Cáceres-Vinueza, Evelyn Frias-Toral, Rosario Suárez, Jorge Daher-Nader, Enrique Flor-Muñoz, Mirna Márquez-Vinueza, Luisa Valeria Guevara-Flores, Yan Duarte-Vera
Bionatura.2023; 8(3): 1. CrossRef - Assessment of common risk factors of diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a Mendelian randomization study
Shuwu Zhao, Yiming Li, Chen Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Inverse association between adult height and diabetes risk in a cohort study of Chinese population
Xiaoli Li, Tiantian Cheng, Lina Leng, Guangyao Song, Huijuan Ma
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender Differences Between the Phenotype of Short Stature and the Risk of Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Adults: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Wei Song, Yaqin Hu, Jiao Yuan, Ying Wei, Zongyou Cheng, Jingdong Liu, Jixiong Xu, Xiaoyu Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - No association between body height and metabolic risk factors in historically short height Asian Indian tribes
Binu Dorjee, Jaydip Sen, Mithun Das, Kaushik Bose, Christiane Scheffler, Gautam Kumar Kshatriya
Human Biology and Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Newly diagnosed diabetes has high risk for cardiovascular outcome in ischemic stroke patients
Kyung-Hee Cho, Sun U. Kwon, Ji Sung Lee, Sungwook Yu, A-Hyun Cho
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Diabetes in Subjects with Positive Fecal Immunochemical Test: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kwang Woo Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Jung Min Moon, Seung Wook Hong, Eun Ae Kang, Jooyoung Lee, Hosim Soh, Seong-Joon Koh, Jong Pil Im, Joo Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1069. CrossRef - The use of Broca index to assess cut- off points for overweight in adults: A short review
Irakoze Laurent, Manirakiza Astère, Banderembako Paul, Nkengurutse Liliane, Yue Li, Qingfeng Cheng, Qifu Li, Xiaoqiu Xiao
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2020; 21(4): 521. CrossRef
- Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
-
- The Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Stroke According to Waist Circumference in 21,749,261 Korean Adults: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Jung-Hwan Cho, Eun-Jung Rhee, Se-Eun Park, Hyemi Kwon, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Hye Soon Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Soon-Jib Yoo, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):206-221. Published online December 27, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0039
- 5,603 View
- 102 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Waist circumference (WC) is a well-known obesity index that predicts cardiovascular disease (CVD). We studied the relationship between baseline WC and development of incident myocardial infarction (MI) and ischemic stroke (IS) using a nationwide population-based cohort, and evaluated if its predictability is better than body mass index (BMI).
Methods Our study included 21,749,261 Koreans over 20 years of age who underwent the Korean National Health Screening between 2009 and 2012. The occurrence of MI or IS was investigated until the end of 2015 using National Health Insurance Service data.
Results A total of 127,289 and 181,637 subjects were newly diagnosed with MI and IS. The incidence rate and hazard ratio of MI and IS increased linearly as the WC level increased, regardless of adjustment for BMI. When the analyses were performed according to 11 groups of WC, the lowest risk of MI was found in subjects with WC of 70 to 74.9 and 65 to 69.9 cm in male and female, and the lowest risk of IS in subjects with WC of 65 to 69.9 and 60 to 64.9 cm in male and female, respectively. WC showed a better ability to predict CVD than BMI with smaller Akaike information criterion. The optimal WC cutoffs were 84/78 cm for male/female for predicting MI, and 85/78 cm for male/female for predicting IS.
Conclusion WC had a significant linear relationship with the risk of MI and IS and the risk began to increase from a WC that was lower than expected.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness of New Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome Optimized for Prediction of Cardiovascular Diseases in Japanese
Yurie Yamazaki, Kazuya Fujihara, Takaaki Sato, Mayuko Harada Yamada, Yuta Yaguchi, Yasuhiro Matsubayashi, Takaho Yamada, Satoru Kodama, Kiminori Kato, Hitoshi Shimano, Hirohito Sone
Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.2024; 31(4): 382. CrossRef - Body mass index, waist circumference and cardiovascular diseases in transitional ages (40 and 66 years)
Jung Eun Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Jin‐Hyung Jung, Yang‐Im Hur, Yang Hyun Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Jang Won Son, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee, Ga Eun Nam
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 369. CrossRef - Risk factors for stroke among anthropometric indices and lipid profiles in the Korean population: a large-scale cross-sectional study
Mi Hong Yim, Young Ju Jeon, Bum Ju Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Research on obesity using the National Health Information Database: recent trends
Eun-Jung Rhee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(2): 35. CrossRef - Association between the weight-adjusted waist index and stroke: a cross-sectional study
Jiayi Ye, Yanjie Hu, Xinrong Chen, Zhe Yin, Xingzhu Yuan, Liping Huang, Ka Li
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased risk of ischemic stroke associated with elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase level in adult cancer survivors: a population-based cohort study
Kyuwoong Kim, Hyeyun Jung, Edvige Di Giovanna, Tae Joon Jun, Young-Hak Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in body composition and subsequent cardiovascular disease risk among 5-year breast cancer survivors
Ji Soo Kim, Jihun Song, Seulggie Choi, Sang Min Park
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Stroke and Abdominal Obesity in the Middle-Aged and Elderly Korean Population: KNHANES Data from 2011–2019
Jong Yeon Kim, Sung Min Cho, Youngmin Yoo, Taesic Lee, Jong Koo Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 6140. CrossRef - Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and related factors in a large sample of antipsychotic naïve patients with first-episode psychosis: Baseline results from the PAFIP cohort
Nathalia Garrido-Torres, Miguel Ruiz-Veguilla, Luis Alameda, Manuel Canal-Rivero, María Juncal Ruiz, Marcos Gómez-Revuelta, Rosa Ayesa-Arriola, Ana Rubio-García, Benedicto Crespo-Facorro, Javier Vázquez-Bourgon
Schizophrenia Research.2022; 246: 277. CrossRef - Development and validation of risk prediction models for stroke and mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes in northern China
X. Shao, H. Liu, F. Hou, Y. Bai, Z. Cui, Y. Lin, X. Jiang, P. Bai, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, C. Lu, H. Liu, S. Zhou, P. Yu
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 46(2): 271. CrossRef - Neck circumference for predicting the occurrence of future cardiovascular events: A 7.6-year longitudinal study
Tingting Hu, Yun Shen, Weijie Cao, Yiting Xu, Yufei Wang, Xiaojing Ma, Yuqian Bao
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(12): 2830. CrossRef - A prospective study of waist circumference trajectories and incident cardiovascular disease in China: the Kailuan Cohort Study
Liang Wang, Yujin Lee, Yuntao Wu, Xinyuan Zhang, Cheng Jin, Zhe Huang, Yixin Wang, Zhiyi Wang, Penny Kris-Etherton, Shouling Wu, Xiang Gao
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2021; 113(2): 338. CrossRef - The Repeatedly Elevated Fatty Liver Index Is Associated With Increased Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Chang-Hoon Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Da Hye Kim, Min-Sun Kwak
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity Degree and Glycemic Status: Factors That Should Be Considered in Heart Failure
Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 529. CrossRef - Exposure-weighted scoring for metabolic syndrome and the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke: a nationwide population-based study
Eun Young Lee, Kyungdo Han, Da Hye Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Development of Myocardial Infarction in Middle-Aged Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Risk Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 636. CrossRef - Obesity Fact Sheet in Korea, 2018: Data Focusing on Waist Circumference and Obesity-Related Comorbidities
Ga Eun Nam, Yang-Hyun Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Yong Gyu Park, Kwan-Woo Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jang Won Son, Seong-Su Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Won-Young Lee, Soon Jib Yoo
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(4): 236. CrossRef - Simply the Best: Anthropometric Indices for Predicting Cardiovascular Disease
Jie-Eun Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(2): 156. CrossRef - Association and Interaction Analysis of Lipid Accumulation Product with Impaired Fasting Glucose Risk: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jian Song, Xue Chen, Yuhong Jiang, Jing Mi, Yuyuan Zhang, Yingying Zhao, Xuesen Wu, Huaiquan Gao
Journal of Diabetes Research.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Letter: Association of Z-Score of the Log-Transformed A Body Shape Index with Cardiovascular Disease in People Who Are Obese but Metabolically Healthy: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2010 (J Obes Metab Syndr 2018;27:158-65
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(2): 139. CrossRef - Response: The Differential Association between Muscle Strength and Diabetes Mellitus According to the Presence or Absence of Obesity (J Obes Metab Syndr 2019;28:46-52)
Bo Kyung Koo
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(4): 297. CrossRef
- Usefulness of New Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome Optimized for Prediction of Cardiovascular Diseases in Japanese

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





